Chapter 1 – Accounting for Partnership : Basic Concepts Questions and Answers: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy (Partnership Accounts)
Class 12 Accountancy chapter 1 - Accounting for Partnership - Questions and Answers of NCERT Book Solutions
1. Mohan and Shyam are partners in a firm. State whether the claim is valid if the partnership agreement is silent in the following matters:
(i) Mohan is an active partner. He wants a salary of Rs. 10,000 per year;
Answer Invalid
I In the absence of partnership agreement, no interest on capital, interest on drawings, salary, commission is to be allowed to partners.
(ii) Shyam had advanced a loan to the firm. He claims interest @ 10% per annum;
Answer Invalid
Interest on partners loan to be allowed @ 6% pa,
(iii) Mohan has contributed Rs. 20,000 and Shyam Rs. 50,000 as capital. Mohan wants equal share in profits.
Answer Valid
Profit and losses are to be shared equally.
(iv) Shyam wants interest on capital to be credited @ 6% per annum.
Answer Invalid
No interest on capital is to be allowed to partners.
2. State whether the following statements are true or false:
(i) Valid partnership can be formulated even without a written agreement between the partners;
Answer True
(ii) Each partner carrying on the business is the principal as well as the agent for all the other partners;
Answer True
(iii) Maximum number of partners in a banking firm can be 20;
Answer True
(iv) Methods of settlement of dispute among the partners can’t be part of the partnership deed;
Answer False
(v) If the deed is silent, interest at the rate of 6% p.a. would be charged on the drawings made by the partner;
Answer False
(vi) Interest on partner’s loan is to be given @ 12% p.a. if the deed is silent about the rate.
Answer False
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question 1. Define Partnership Deed.
Answer. A partnership deed is a agreement among the partners which contains ai! the terms of the Partnership. It generally contains the details about all the aspects affecting the relationship between the partners including the objective of business, contribution of capita! by each partner, -atio in which the profits and the losses will be shared by the partners and entitlement of partners to interest on capital, interest on loan etc.
Question 2. Why it is considered desirable to make the partnership agreement in writing?
Answer As .per Partnership Act 1932 it is not necessary that a partnership agreement must be in writing but still it is always suggested that it should be in written form Because today there are very good relationship among the partners but n future if there may be any dispute regarding any issue, a written partnership agreement will help in avoiding disputes and misunderstandings among the partners.
Question 3. List the items which may be debited or credited in capital accounts of the partners when
(i) Capitals are fixed
(ii) Capitals are fluctuating
Answer. (i)When capitals are fixed, the following items will be debited or^ credited in partners capital account
(i) 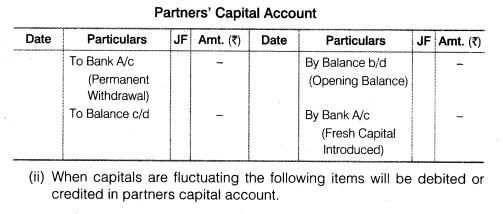
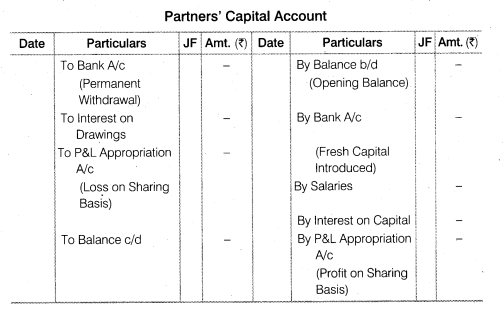
Question 4. Why is Profit and Loss Adjustment Account prepared? Explain.
Answer. Profit and loss adjustment account is prepared to record those transaction or omissions and errors which were left while preparing the final accounts and they are found after the final accounts have been prepared and the profits distributed among the partners. The omission may be in respect of interest on capital, interest on drawings, interest on partners’ loan, partner’s salary, partner’s commission or outstanding expenses. There may also be some changes in the provisions of partnership deed or system of accountings having impact with retrospective effect. All these acts of omission and commission need adjustments for correction of their impact. These omission errors and corrections can be recorded in partners’ capital account directly but still it seems convenient to prepare the profit and loss adjustment account.
Question 5. Give two circumstances under which the fixed capitals of partners may change.
Answer. Under the fixed capital method the capital of partners may change in the following two circumstances
(i) First, when fresh capital is introduced by the partner with the consent of other partners.
(ii) Second, when a part of capital is withdrawn by the partner with the consent of other partners.
Question 6. If a fixed amount is withdrawn on the first day of every quarter, for what period the interest on total amount withdrawn will be calculated?
Answer. When fixed amount of money is withdrawn quarterly, it can be withdrawn either at the beginning or at the end of each quarter, if the amount is withdrawn at the end of each quarter, the interest is calculated on the total money withdrawn during the period of seven and half months .
Question 7. In the absence of partnership deed, specify the rules relating to the following
(i) Sharing of profits and losses (ii) Interest on partner’s capital
(iii) Interest on partner’s drawings (iv) Interest on partner’s loan
(v) Salary to a partner
Answer :(i)Sharing of Profit and Losses
In the absence of partnership deed profit sharing ratio among the pad maw will be equal.
(ii) Interest on Partner’s Capital
In the absence of paonemnio oeeu interest on partners capital will not be given.
(iii) Interest on Partner’s Drawings
In the absence of partnership deed no interest will be charged on partners drawings .
(iv) Interest on Partners Loan
In the absence of partnership deed if partner gives any loan to the firm he/she will be entitled to get fixed percentage of interest @6% of annum.
(v) Salary of Partner
In the absence of the patnership deed a partner will be entitled for getting any salary for his work even if the other are non working.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is partnership? What are its chief characteristics? Explain.
Answer. According to the Section 4 of the Partnership Act, 1932 Partnership is an agreement between two or more persons who have agreed to share profits or losses of a business that will be carried by all or any one of them acting for all. Person who joined their hands to set up the business are called ‘partners individually and ‘firm’ collectively and the name under which they carry out their business is termed as ‘firm name’. The following are the important characteristics of partnership
(i) Two or More Persons
In order to form partnership, there should be at least two person coming together for a common goal In other words, the minimum number of partners in a firm can be two. There is however, a limit on their maximum number, if a firm is engaged in the banking business, it can have a maximum of ten partners while in case of any other business, the maximum number of partners can be twenty.
(ii) Partnership Deed
A partnership deed is an agreement among the partners which contains all the terms of the partnership. It generally contains the details about all the aspects affecting the relationship between the partners including the objective of business, contribution of capital by each partner, ratio in which the profits and the losses will be shared by the partners and entitlement of partners to interest on capital, interest on loan, etc.
(iii) Business
One of the important characteristics of a partnership is that it is formed to carry out a legal business. Partnership in case of illegal business is not valid.
(iv) Sharing of Profit
In case of a partnership the partners are suppose to share profit or loss on an agreed ratio or as per the provisions of the Partnership Act, 1932, as per which they will share profit equally.
(v) Liability
In the case of a partnership liability of partners are unlimited. If there is any obligation against the third party the partner will have to pay it out of his personal property.
Question 2. Discuss the main provisions of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932 that are relevant to partnership accounts if there is no partnership deed.
Answer It is always suggested that there must be a partnership deed among the partners before getting into any partnership venture. But sometimes a partnership is started without signing any such document. In this case the rules of partnership will be applicable as per the provisions of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932. The following are the provisions that are relevant to the partnership accounts in absence of partnership deed.
(i) Profit Sharing Ratio When a partnership deed is not made or even if it is made and silent on sharing of profit or losses among the partners of a firm, then according to the Partnership Act 1932, profits and losses are to be shared equally among all the partner of the firm.
(ii) Interest on Capital When there is absence of partnership deed or the partnership deed is silent on the issue related to interest on partner’s capital, then according to the Partnership Act 1932, no interest on partners’ capital will be provided. However, if they mutually agree on this issue than they are free to give interest on capital out of the profit of the firm.
(iii)Interest on Drawings there is no partnership Peed the issue ‘elated h die interest on drawing will be handled according to the provisions Partnership Act. 1932 According sc which no Interest on drawing will be charge loan the orders on withdraw in the form of drawings.
(iv) Interest on Partner’s Loan When there is no partnership deed among the partners or the partnership deed is silent on interest on partner’s loan then according to the Partnership Act, 1932. the partners are entitled for 6% pa interest on the loan forwarded by them to the firm
(v) Salary to Partner When partnership deed is not there or it is silent on the issue related to salary to a partner, then as per the rules of the partnership Act. 1932. no partner will be entitled to any salary.
Question 3. Explain why it is considered better to make a partnership agreement in writing.
Answer As per Partnership Act. 1932, it is not necessary that a partnership agreement must be in writing but still it is always suggested that it should be in written form. Because today there are very good relationship among the partners but in future there may be any dispute regarding any Issue a written partnership agreement will help in avoiding dusputes and misunderstandings among the partners.
In this way a written partnership deed is more desirable than the ora agreements. A written partnership agreement ensures the smooth functioning of the business of the partnership firm It aiso helps in settling the disputes among the partners. Moreover a duly signed and registered partnership deed can be used as evidence in the court of law. Therefore, it s desirable to form partnership deed in writing because of the moots associated with written documents over its oral counterparts.
Question 4. Illustrate how interest on drawings will be calculated under various situations.
Answer When a partner withdraws any amount, either in cash or in any other form, from the firm for his/her personal use, then it is termed as drawings. The interest charged by the firm on the amount of drawings is termed as interest on drawings. The method of calculating interest on drawings depends on the information available for time and frequency of the drawings made by the partner. The following different situations of drawings made illustrate the calculation of interest charged on drawings.
Situation I When ail the information regarding amount, date and rate of interest on drawings is given
When a partner withdrew Rs 10,000 on July 01 and interest on drawings is charged at 12% pa and the firm closed its books on December 31 every year then interest on drawings amount to Rs 600.
.png)
Situation(II When information regarding amount, rate of interest on drawings is given
Case I Sometimes amount and rate of interest on drawings (per annum) is given but date is not mentioned
in this case when the details regarding the amount of drawings and rate of interest on drawings (pa) is given but the date of drawings is not given then interest will be charged on average basis and the period of drawings will be taken as 6 months
.png)
Case II Sometimes the amount and rate of is interest on drawings is given but the date and per anum rate of interest is not mentioned.
In this case when the date and the rate of interest aim given but per annum is not specified, then annual interest is charged.
e.g., If a partner withdrewRs 10 000 and interest rate is 12%, then the interest on drawings amounts to Rs.12,000.
.png)
Situation III When a fixed amount is withdrawn at regular interval
Case I Sometimes a fixed amount is withdrawn at the beginning of each month and the rate of interest is given then the interest is calculated for 6 5 months.
e.g.. If a partner withdraws Rs1,000 in the beginning of every month and the rate of interest is 12% pa, then the interest on drawings amount to RS 780.
.png)
Case II Sometimes a fixed amount is withdrawn at the end of each month and the rate of interest is given then the interest is calculated for 5.5 months.
e.g.. if a partner withdraws Rs 1.000 at the end of each month arid rate of interest is 12% pa then the interest on drawings amount to Rs 660.
.png)
Case III Sometimes a fixed amount is withdrawn at the mid of each month and the rate of interest is given then the interest is calculated for 6 months.
e g. if a partner.withdraws Rs.1,000 on 15th of every month and the rate of in’crest is 12% pa then the interest on drawings amount to Rs 720.
.png)
Case IV If a fixed amount is withdrawn in the beginning of every quarter then the interest is calculated for 7.5 months.
e.g.. If a partner withdraws Rs.5,000 in the beginning of every quarter and the rate of interest is 12% pa then the interest on drawings amount to Rs 1,800.
.png)
Case V If a fixed amount is withdrawn at the end of every quarter, then the interest is calculated for 4.5 months.
e.g., If a partner withdraws Rs. 5,000 at the end of every quarter and the rate of interest is 12% pa then the interest on drawings amounts to Rs. 900
.png)
Situation IV When different amount is at different intervals
When different amount is withdrawn by a partner at different dates then the interest is calculated by product method. The period of drawings is calculated from the date of withdrawal to the last date of the accounting year,
e.g., A partner withdraws?6,000 on March 01, Rs.4,000 on June 01, Rs.5,000 on Aug 30 and Rs.2,000 on Nov 30 and the rate of interest on drawings is 12% pa. The firm closes its book on December 31.
.png)
Question 5. How will you deal with a change in profit sharing ratio among existing partners? Take imaginary figures to illustrate your answer.
Answer Change in the profit sharing ratio occurs only in case of the admission, retirement or death of a partner or sometimes due to the general agreement among the partners in which they may decide to change the profit sharing ratio. There may be number of issues that should be considered during the change in the profit sharing ratio such as goodwill, reserves and accumulated profits, profit or loss on the revaluation of assets and liabilities and adjustment of capital, etc. As far as the issue related to general reserve is concerned it is basically the accumulated profits (if any) and profit (or loss) on revaluation of assets and liabilities and should be distributed in the partner’s capital account in partners old profit sharing ratio. Sometimes the existing partners may decide to change the profit sharing ratio then some partners gain at the cost of other partners. In other words one partner gain and other one sacrifice equal to the gain. In that case the former should compensate the latter. Therefore, the gaining partner’s capital account’s are debited to the extent of their gain and sacrificing partner’s capital accounts are credited to the extent of their sacrifice .The following journal entry is passed
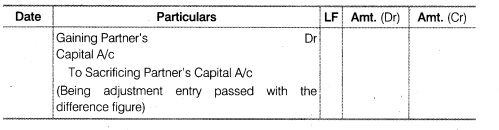
Example Ram. Mohan and Shyam are partners in a firm sharing profit and loss in 3 2 :1 ratio. They decide to share profit and loss equally in future. On dm: date, the books of the firm showsRs.2.40.000 as general reserve, profit on ^evaluation of Plant and Machinery Rs.60.000. The following adjustment entry is passed through the capital accounts without affecting the books of accounts.
 png.png)
Hence, in the above example. Shyam gains at the cost of Ram. so the Ram needs to be compensated by Shyam with the amount of Rs.50.000. The following adjustment entry is passed.

(iii) Maximum number of partners in a banking firm can be 20
Last Updated on: December 05, 2025
