Chapter 11 – Alcohols Phenols and Ether Questions and Answers: NCERT Alcohols Phenols and Ether for Class 12 Chemistry
Class 12 Chemistry chapter 11 - Alcohols Phenols and Ether - Questions and Answers of NCERT Book Solutions.
11.1. Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
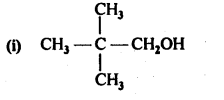
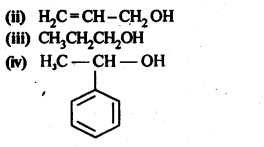
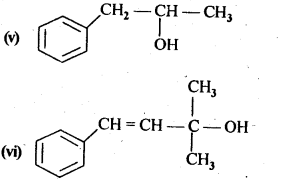
Ans: Primary alcohols: (i), (ii), (iii)
Secondary alcohols: (iv), (v)
Tertiary alcohols: (vi)
11.2. Identify aliylic alcohols in the above examples.
Ans: (ii) and (iv) i.e. H2C=CH – CH2OH and
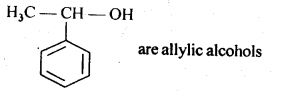
11.3. Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system.
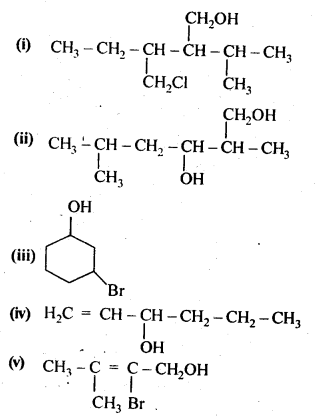
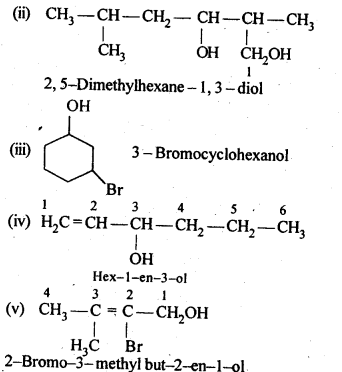
Ans:
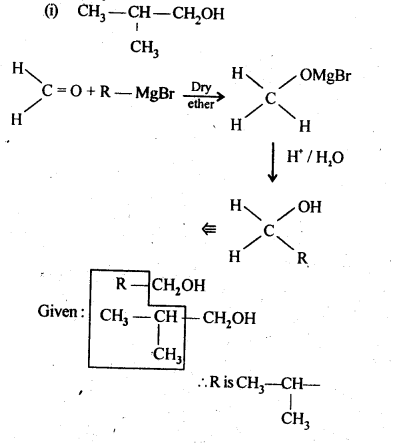
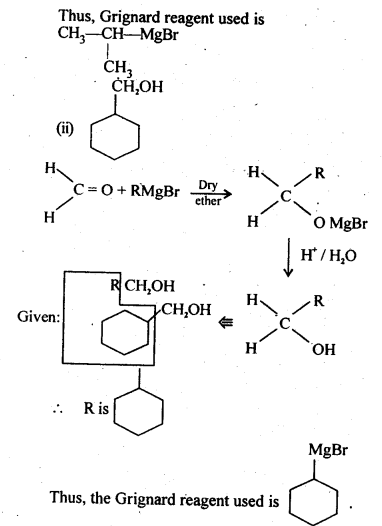
11.4. Show how are the following alcohols prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent on methanal ?

Ans:
11.5. Write structures of the products of the following reactions:
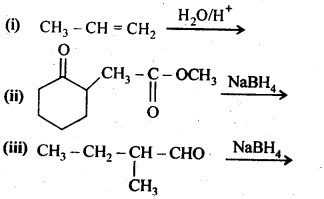
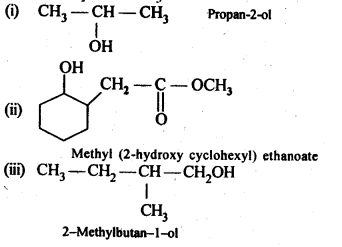
Ans:
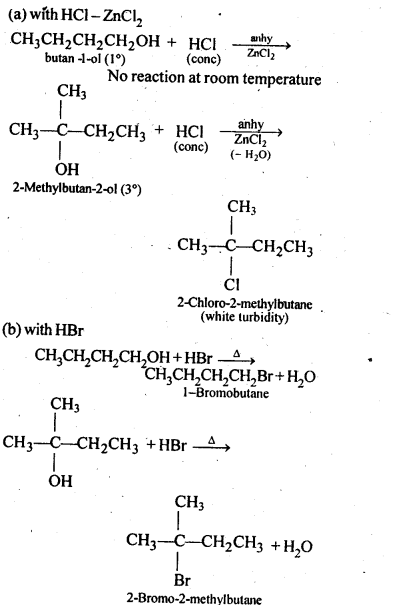
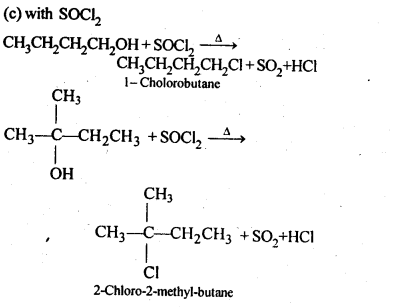
11.6. Give structures of the products you would expect when each of the following alcohol reacts with (a)HCl-ZnCl2 (b)HBrand (c) SOCl2
(i)Butan-1-ol>
(ii)2-Methylbutan-2-ol
Ans:
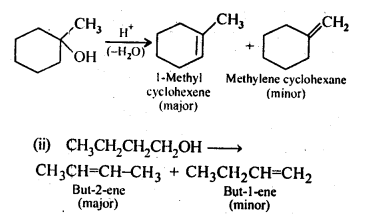
11.7. Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration of
(i) 1-nicthylcyclohcxanoland
(ii) butan-1-ol
Ans:
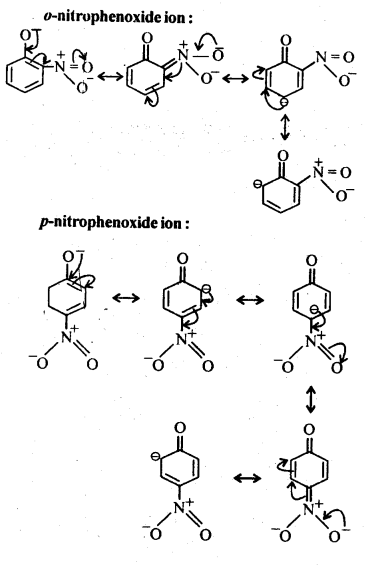
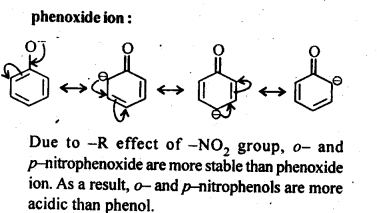
11.8. Ortho and para nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol. Draw the resonance structures of the corresponding phenoxide ions.
Ans:The resonance structures of o-and p- nitrophenoxide ions and phenoxide ion are given below:
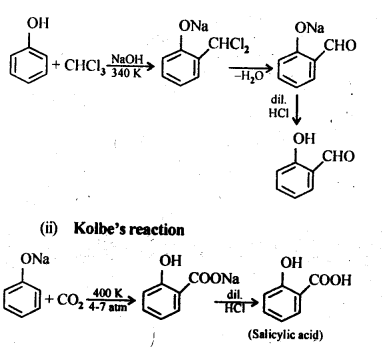
11.9; Write the equations involved in the following reactions:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(ii) Kolbe’s reaction
Ans: (i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
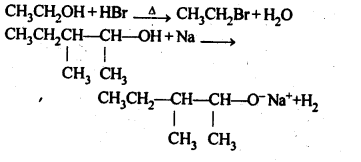
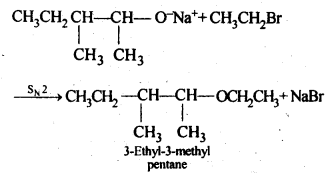
11.10. Write the reactions of Williamson synthesis of 2-ethoxy-3-methylpentane starting from ethanol and 3-methylpentan-2-ol.
Ans: In Williamsons’s synthesis, the alkyl halide should be primary. Thus, the alkyl halide should be derived from ethanol and the alkoxide ion from 3-methylpentan-2-ol. The synthesis is as follows
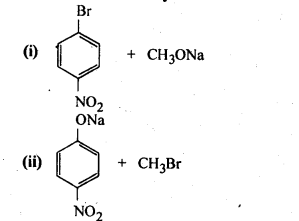
11.11. Which of the following is an appropriate set of reactants for the preparation of l-methoxy-4- nitrobenzene and why?
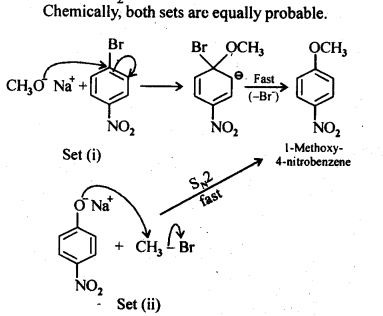
Ans:
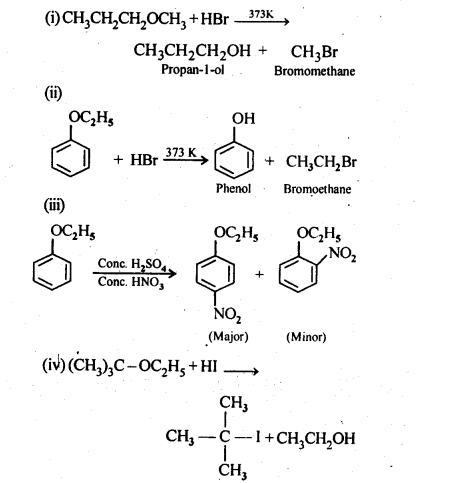
11.12. Predict the products of the following reactions:>
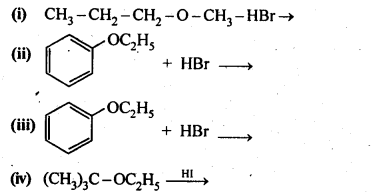
Ans:
Last Updated on: Feb 26, 2024
