Chapter 3 – Electrochemistry Questions and Answers: NCERT Electrochemistry for Class 12 Chemistry
Class 12 Chemistry chapter 3 - Electrochemistry - Questions and Answers of NCERT Book Solutions.
3.1. How would you determine the standard electrode potential of the system Mg2+1 Mg?
Ans: A cell will be set up consisting of Mg/MgSO4 (1 M) as one electrode and standard hydrogen electrode Pt, H, (1 atm)H+/(l M) as second electrode, measure the EMF of the cell and also note the direction of deflection in the voltmeter. The direction of deflection shows that e-1 s flow from mg electrode to hydrogen electrode, i.e., oxidation takes place on magnesium electrode and reduction on hydrogen electrode. Hence, the cell may be represented as follows :
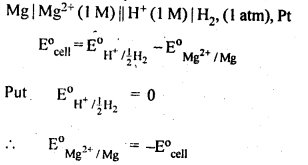
3.2. Can you store copper sulphate solutions in a zinc pot?
Ans: Zn being more reactive than Cu, displaces Cu from CuSO4 solution as follows:Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) –> ZnSO4(ag)+Cu (s)

3.3. Consult the table on standard electrode potentials and suggest three substances that can oxidise Fe2+ ions under suitable conditions.
Ans. The oxidation of Fe2+ ions to Fe3+ ions proceeds as follows :
Fe2+ → 3+ + e– ; E∘OX = – 0·77 V
Only those substances can oxidise Fe2+ ions to Fe3+ ions which can accept electrons released during oxidation or are
placed above iron in electrochemical series. These are : Cl2(g), Br2(g) and Cr2O2−7 ions (in the acidic medium).
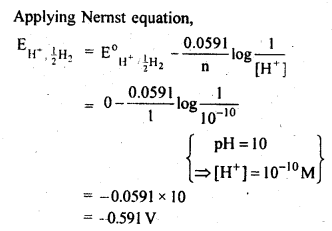
3.4. Calculate the potential of hydrogen electrode in contact with a solution whose pH is 10.
Ans. For hydrogen electrode,H+ + e– —>1/2 H2,
3.5. Calculate the emf of the cell in which the following reaction takes place:
Ni(s)+2Ag+ (0.002 M) -> Ni2+ (0.160 M)+2Ag(s) Given that E(-)(cell) = 1.05 V .
Ans:

3.6. The cell in which the following reaction occurs: 2Fe3+ (aq) + 2I– (aq) —> 2Fe2+ (aq) +I2 (s) has E°cell=0.236 V at 298 K. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy and the equilibrium constant of the cell reaction.
Ans:
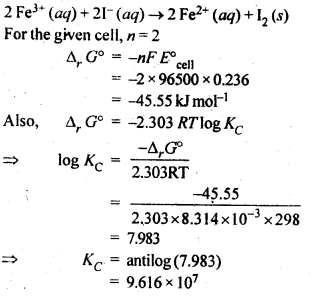
3.7. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
Ans: The conductivity of a solution is linked with the number of ions present per unit volume. With dilution, these decrease and the corresponding conductivity or specific conductance of the solution decreases.
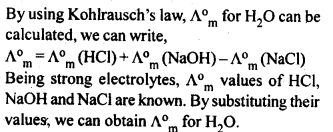
3.8. Suggest a way to determine the value of water.
Ans:
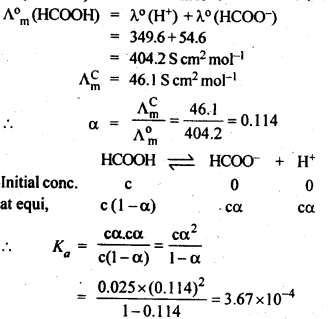
3.9. The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L-1 methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm2 mol-1. Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant Given λ°(H+)=349.6 S cm2 mol-1 andλ°(HCOO-) = 54.6 S cm2 mol-1
Ans:
3.10. If a current of 0.5 ampere flows through a metallic wire for 2 hours, then how many electrons would flow through the wire?
Ans:
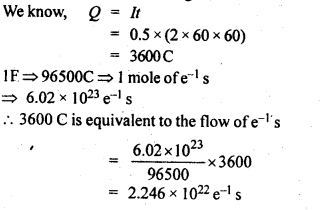
3.11. Suggest a list of metals which can be extracted electrolytically.
Ans: The highly reactive metals having large -ve E° values, which can themselves act as powerful reducing agents can be extracted electrolytically. The process is known as electrolytic reduction. For details, consult Unit-6. For example, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium etc.
3.12. Consider the reaction: Cr2O72--+ 14H+ + 6e- -> 2Cr3+ + 7H2O What is the quantity of electricity in coulombs needed to reduce 1 mol of Cr2O72- ?
Ans:
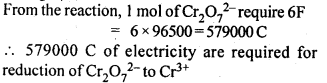
3.13. Write the chemistry of recharging the lead storage battery, highlighting all the materials that are involved during recharging.
Ans: A lead storage battery consists of anode of lead, cathode of a grid of lead packed with lead dioxide (PbO2) and 38% H2SO4 solution as electrolyte. When the battery is in use, the reaction taking place are:
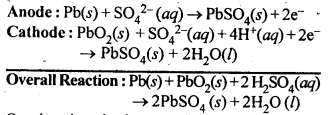
On charging the battery, the reverse reaction takes place, i.e., PbSO4 deposited on electrodes is converted back to Pb and PbO2 and H2SO4 is regenerated.
3.14. Suggest two materials other than hydrogen that can be used as fuels in the fuel cells.
Ans: Methane (CH4) and methanol (CH3OH) can also be used as fuels in place of hydrogen in the fuel cells.
3.15. Explain how rusting of iron is envisaged as setting up of an electrochemical cell.
Ans: The water present on the surface of iron dissolves acidic oxides of air like CO2 , SO2 , etc. to form acids which dissociate to give H+ ions :
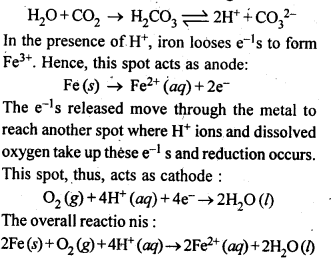
Thus, an electrochemical cell is set up on the surface.Ferrous ions are further oxidised by atmospheric oxygen to ferric ions which combine with water to form hydrated ferric oxide, Fe2O3. xH2O, which is rust.
Last Updated on: Feb 23, 2024
