Chapter 5 – Surface Chemistry Questions and Answers: NCERT Surface Chemistry for Class 12 Chemistry
Class 12 Chemistry chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry - Questions and Answers of NCERT Book Solutions.
5.1. Write any two characteristics of Chemisorption.
Ans: Pt and Pd form inert electrodes, i.e., they are not attacked by the ions of the electrolyte or the products of electrolysis. Hence, they are used as electrodes for carrying out electrolysis.
5.2. Why does physisorption decrease with the increase of temperature?
Ans: Physisorption is an exothermic process :
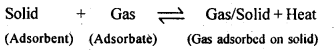
According to Le-Chatelier’s principle, if T is increased, equilibrium shifts in the backward direction i.e., gas is released from the surface of solid.
5.3. Why are powdered substances more effective as adsorbents than their crystalline forms?
Ans: The powdered form of the adsorbent has greater surface area as compared to the crystalline form. This will be therefore, more effective as adsorbent.
5.4. In Haber’s process, hydrogen is obtained by reacting methane with steam in presence of NiO as catalyst. The process is known as steam reforming. Why is it necessary to remove CO when ammonia is obtained by Haber’s process?
Ans: CO acts as a poison for the catalyst used in the manufacture of NH3 by Haber’s process. Hence, it is necessary to remove it.
5.5. Why is the ester-hydrolysis slow in the beginning and becomes faster after sometime?
Ans: The ester hydrolysis takes place as follows :
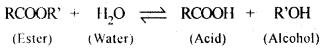
The acid produced in the reaction acts as an auto catalyst for the reaction. Hence, the reaction becomes faster after some time.
5.6. What is the role of desorption in the process of catalysis?
Ans: In the heterogeneous catalysis carried over metal surface, adsorbed reactant species combine to form the products. They have to be desorbed from the surface so that more the reactants may be accommodated on the surface of the catalyst. Therefore, desorption has a specific role to play in the process of catalysis.
5.7. What modification can you suggest in the Hardy Schulze, law?
Ans: According to Hardy Schulze law, the coagulating ion has charge opposite to that on the colloidal particles. Hence, the charge on colloidal particles is neutralized and coagulation occurs.
The modification to this law is :
When oppositely charged sols are mixed in proper proportions to neutralize the charges of each other, coagulation of both the sol occurs.
5.8. Why is it essential to wash a precipitate with water before estimating it quantitatively?
Ans: Precipitates are generally formed in the ionic reactions. Some ions of the reactants may be adsorbed or may stick on the surface of the particles of the precipitate. These can be removed by washing the precipitate repeatedly with water. In case these ions are not removed, they may introduce some error in weighing when the precipitate is estimated quantitatively.
Last Updated on: Feb 23, 2024
