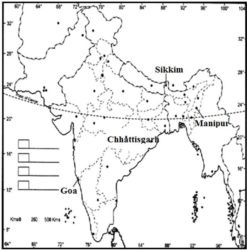
1. Locate the following States on a blank outline political map of India: Manipur, Sikkim, Chhattisgarh and Goa.
Answer :-
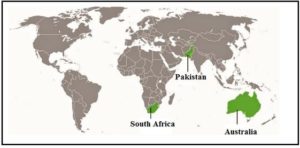
2. Identify and shade three federal countries (other than India) on a blank outline political map of the world.
Answer:
3. Point out one feature in the practice of federalism in India that is similar to and one feature that is different from that of Belgium.
Answer:
Feature in the practice of federalism in India that is similar to that of Belgium – the central government has to share its powers with the regional or the state governments.
Feature in the practice of federalism in India that is different from that of Belgium – Unlike India, Belgium has a community government in addition to the central and the state government.
4. What is the main difference between a federal form of government and a unitary one? Explain with an example.
Answer:
| Federal form of government | Unitary form of government |
| There is a sharing of power between the state and the central governments.
For example – In India, there is union government at the centre and the state governments at the state level. |
In this form of government, the central government has all the powers and there is no role of the state governments.
For example – In Sri Lanka and Britain, the national government has all the powers. |
5. State any two differences between the local government before and after the Constitutional amendment in 1992.
Answer:
| Local government before 1992 | Local government after 1992 |
| 1. Elections to the local governments were not held regularly. | 1. Now it is constitutionally mandatory to hold regular elections to local government bodies. |
| 2. Local governments did not have any powers or resources of their own. | 2. The State governments are required to share some powers and revenue with local government bodies. |
6. Fill in the blanks:
Since the United States is a ___________________ type of federation, all the constituent States have equal powers and States are ______________vis-à-vis the federal government. But India is a _____________________ type of federation and some States have more power than others. In India, the ____________ government has more powers.
Answer:
Since the United States is a coming together type of federation, all the constituent States have equal powers and States are strong vis-à-vis the federal government. But India is a holding together type of federation and some States have more power than others. In India, the central government has more powers.
7. Here are three reactions to the language policy followed in India. Give an argument and an example to support any of these positions.
Sangeeta: The policy of accommodation has strengthened national unity.
Arman: the Language-based States have divided us by making everyone conscious of their language.
Harish: This policy has only helped to consolidate the dominance of English over all other languages.
Answer:
Sangeeta’s view that the policy of accommodation has strengthened national unity is a correct reaction to the language policy followed in India. There are several regional or local languages spoken in the country. By introducing the language policy, the Indian government has given equal status to all the languages in the country. Due to this policy, India stands in unity with states having different languages.
8. The distinguishing feature of a federal government is:
(a) The national government gives some powers to the provincial governments.
(b) Power is distributed among the legislature, executive and judiciary.
(c) Elected officials exercise supreme power in the government.
(d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government
Answer: (d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government
9. A few subjects in various Lists of the Indian Constitution are given here. Group them under the Union, State and Concurrent Lists as provided in the table below.
A. Defence; B. Police; C. Agriculture; D. Education; E. Banking; F. Forests; G. Communications; H. Trade; I. Marriages
Union List
State List
Concurrent List
Answer:
| Union List | Defence, Banking, Communications |
| State List | Police, Agriculture, Trade |
| Concurrent List | Education, Forests, Marriages |
10. Examine the following pairs that give the level of government in India and the powers of the government at that level to make laws on the subjects mentioned against each. Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
| (a) State government | State List |
| (b) Central government | Union List |
| (c) Central and State governments | Concurrent List |
| (d) Local governments | Residuary powers |
Answer:
(d) Local governments Residuary powers
11. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
| List-I | List-II |
| 1. Union of India | A. Prime Minister |
| 2. State | B. Sarpanch |
| 3. Municipal Corporation | C. Governor |
| 4. Gram Panchayat | D. Mayor |
Codes:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| (a) | D | A | B | C |
| (b) | B | C | D | A |
| (c) | A | C | D | B |
| (d) | C | D | A | B |
Answer:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| (c) | A | C | D | B |