How to use this map
Two imaginary sets of lines - the longitudes and latitudes - drawn around the world to make a grid give us the geographical coordinates of any place. We can find out how far north, east, west, and south that place is on earth by referring to these coordinates.
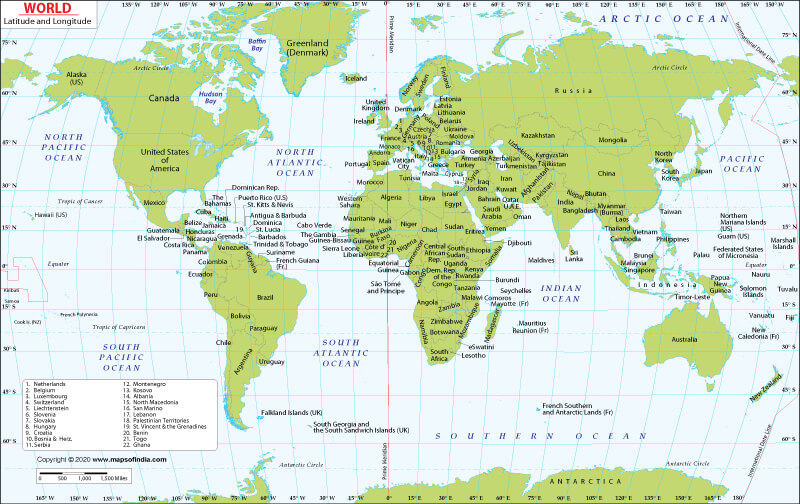
This map displays the geographical coordinates - the latitude and the longitude - of the world. It also shows the countries along with the latitudes and longitudes. Additionally, the oceans (the North Atlantic, the South Atlantic, the North Pacific, the South Pacific, the Indian, the Southern, and the Arctic) are displayed. The map is a useful resource for schoolchildren and a helpful aid for parents and teachers.
This concept of using such imaginary lines was first developed by the ancient Greek philosopher Eratosthenes in the 3rd century BCE. The Prime Meridian was established in 1851 at the royal observatory at Greenwich, London. Relative to this longitude, the time of the entire world is decided.
Latitude
Latitudes are horizontal lines running from east to west. The Equator, which cuts the world at the center, is given the value 0°. All other lines of latitudes run parallel to the Equator and are numbered in degrees north or south of the Equator. The North and South Poles are at either end. The North Pole is at 90° north and the South Pole at 90° south.
The Equator divides the earth into two hemispheres. The area north is the Northern hemisphere, and the area south is the Southern hemisphere. Most of the landmass on earth is in the Northern Hemisphere. Europe and North America are the only continents that lie entirely in the Northern Hemisphere, while Australia and Antarctica are the only continents that lie wholly in the Southern Hemisphere. Asia, South America, and Africa are spread out between both hemispheres. Four of the earth's oceans (the South Pacific, South Atlantic, Southern, and Indian) are in the Southern Hemisphere.
The Arctic Circle, with its value at 66° 33' N, runs parallel to the Equator. The area north of this is the Arctic Polar Region. The Antarctic Circle, with its value at 66°33' S, runs parallel to the Equator, and the area south of this is the Antarctic Polar region.
The Tropic of Cancer, at a value of 23° 26' N, passes through the Northern Hemisphere. Similarly, the Tropic of Capricorn, at a value of 23° 26' S, passes through the Southern Hemisphere. The region between these two, centered on the Equator, is the tropical region.
Some of the countries that fall in the northern hemisphere are the USA, Italy, China, and India, and some of the countries that fall in the Southern hemisphere are Namibia, Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Madagascar, and Australia. Some countries, such as Brazil, Congo, and Indonesia, straddle both hemispheres.
Longitude
Longitudes are vertical lines running from north to south. The Prime Meridian, which passes through Greenwich, London, is given the value 0°. All other lines of the longitude are numbered in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian. The imaginary line connecting the poles and opposite the Prime Meridian is given the value 180°.
The Prime Meridian divides the earth into eastern and western hemispheres, and of these, Asia and Africa are part of the eastern hemisphere. At the same time, the Americas (North and South) are part of the Western hemisphere. The International Dateline also corresponds to the 180° longitude, though it zigzags to allow for local geographical considerations. This has the primary objective of separating two consecutive calendar days. The date in the eastern hemisphere is one day ahead of the date in the western hemisphere.
Historical aspects
During 2000 BCE, the Egyptians started a phase that included the use of a grid system for the purpose of surveying and mapping. The proposition of the concept of latitudes and longitudes was first done by the Greek mathematician and geographer Eratosthenes. He developed a system of parallel lines (latitudes) and meridian lines (longitudes) to measure the Earth’s circumference. Further advancements were made by Hipparchus, who is credited with dividing the circle into 360 degrees, with each degree consisting of 60 minutes and each minute consisting of 60 seconds. This system has also helped in developing the modern-day understanding of how time varies on different continents and nations across the world.
After the subsequent developments, there was a major breakthrough through the ideas of Ptolemy. A man of Greek origin, he developed the concept of longitude and used the system of latitudes and longitudes to create a map. This was publicized through his work, “Geographia,” which influenced geographers and cartographers for the longest period of time. An arena long dominated by the Greeks saw the coming of the age of Flemish influence. Gerardus Mercator developed the Mercater projection that was used to preserve straight lines. He was also one of the first known people to have used the system of latitudes and longitudes for the purpose of navigation.
In the 17th century, Dutch scientist Williebrord Snellius developed and advanced the method of triangulation for measuring distances. Triangulation employs the principles of trigonometry to calculate the distance between the sides of a triangular route so that estimates can be made for better navigation. John Harrison, an English clockmaker, invented the marine chronometer, which enabled sailors to determine their longitude at sea. He also built the first practical seawatch that was compact and portable, as well as aided in the functioning of the ships.
The modern era, however, has witnessed new resolutions added to the archaic uses of the concept. The development of telegraphy, radio navigation, and satellite technology improved the measurement of the horizontal and vertical frames of reference. During the 1970s, the Global Positioning System came into existence, and by the 1990s, the advancement was so rapid that it began providing real-time accurate locations to the users. At the beginning of the 21st century, the advent of smartphones and smart gadgets led to the popularization of latitude and longitude.
Significance of Latitudes and Longitudes
These coordinates are employed by people on a daily basis for a variety of purposes. The GPS (Global Positioning System) that is often used in our phones relies on a variety of satellites to give us our location in association with latitudes and longitudes. They also aid pilots and sailors to steer the ship in their directions and to take the best-suited course for the journey. They also make use of maps designed by cartographers. Such people themselves design the graphical representation of the world in the form of a map relative to its extent at the two coordinates. Geographic Information Systems are used to analyze and visualize geospatial data, which aids in studying population dynamics, natural resource distribution, and climate patterns.
The practical applications can be discovered in our day-to-day lives. The location-based system is also employed in the processing of emergency calls to locate the caller and deploy the nearest rescue forces. Logistics and delivery-based companies also use the same approach to track shipments and deliver the packages to their destined locations.
Developing an understanding of the system also aids in the better estimation of climate and weather patterns. Westerly winds are most common in the mid-latitude regions, and these blow from the west to the east. Another feature that is common is that tornadoes are also common in the mid-latitude regions, whereas hurricanes form near the equator and move westward. On the other hand, blizzards occur in the polar regions. Climate scientists also use it to make an estimation of weather patterns and track any disturbances.
Along with this, geocaching is also a popular activity where participants use latitude and longitude coordinates to find hidden objects called “geocaches.” These can be employed in various locations, such as the wilderness, urban areas, and rural areas. This principle has also been used in the design of various applications and games, the objectives of which are to find hidden objects or to locate someone.
FAQs
Q1: What is the basic difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude measures the north-south position, whereas longitude measures the east-west position.
Q2: What are its units of measurement?
Degrees(°), minutes(’), and seconds (”), with decimal degrees, are commonly used.
Q3: Can latitudes and longitudes be negative?
Yes, the latitudes south of the equator and the longitudes to the west of the Prime Meridian can be negative.
Q4: How are time zones related to longitudes?
Longitude aids in the determination of time zones, as the increase in each hour represents 15° of longitude.
Q5: Can latitudes and longitudes be used for navigation without technology?
Yes, they can be used through dead reckoning and celestial navigation methods.
Last Updated on: February 19, 2026